Natural selection only acts on the population’s heritable traits: selecting for beneficial alleles and thus increasing their frequency in the population, while selecting against deleterious alleles and thereby decreasing their frequency. Scientists call this process adaptive evolution. Natural selection does not act on individual alleles, but
Change in allele frequencies due to natural selection – YouTube
5.0 (5 reviews) Natural selection changes allele frequencies because some _______ survive and reproduce more successfully than others. Click the card to flip 👆 individuals Click the card to flip 👆 1 / 32 Flashcards Learn Test Match Q-Chat Created by shanksnicky Students also viewed Ch. 23 AP Bio Quiz 5 terms mattchuritch Preview

Source Image: chegg.com
Download Image
Evolution by natural selection occurs when certain genotypes produce more offspring than other genotypes in response to the environment. It is a non-random change in allele frequencies from one generation to the next.

Source Image: nbcnews.com
Download Image
Evolution of Populations Oct 31, 2023If we also know that the frequency of the I B allele in this population is 0.14, then the frequency of the i allele is 0.6, which we obtain by subtracting all the known allele frequencies from 1 (thus: 1 – 0.26 – 0.14 = 0.6). A change in any of these allele frequencies over time would constitute evolution in the population.

Source Image: johnhawks.net
Download Image
Natural Selection Changes Allele Frequencies In Populations Because Some
Oct 31, 2023If we also know that the frequency of the I B allele in this population is 0.14, then the frequency of the i allele is 0.6, which we obtain by subtracting all the known allele frequencies from 1 (thus: 1 – 0.26 – 0.14 = 0.6). A change in any of these allele frequencies over time would constitute evolution in the population. Figure 1. Different types of natural selection can impact the distribution of phenotypes within a population. In (a) stabilizing selection, an average phenotype is favored. In (b) directional selection, a change in the environment shifts the spectrum of phenotypes observed. In (c) diversifying selection, two or more extreme phenotypes are
Top 10 discoveries about ancient people from DNA in 2023
11.2: Mechanisms of Evolution. The Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium principle says that allele frequencies in a population will remain constant in the absence of the four factors that could change them. Those factors are natural selection, mutation, genetic drift, and migration (gene flow). In fact, we know they are probably always affecting populations. 3 Major factors that alter allele freq’s and bring about evolutionary change 1. Natural Selection – alleles passed to next generation in proportions diff. – ppt download

Source Image: slideplayer.com
Download Image
IB HL 10.3.U1 & 10.3.U2 11.2: Mechanisms of Evolution. The Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium principle says that allele frequencies in a population will remain constant in the absence of the four factors that could change them. Those factors are natural selection, mutation, genetic drift, and migration (gene flow). In fact, we know they are probably always affecting populations.
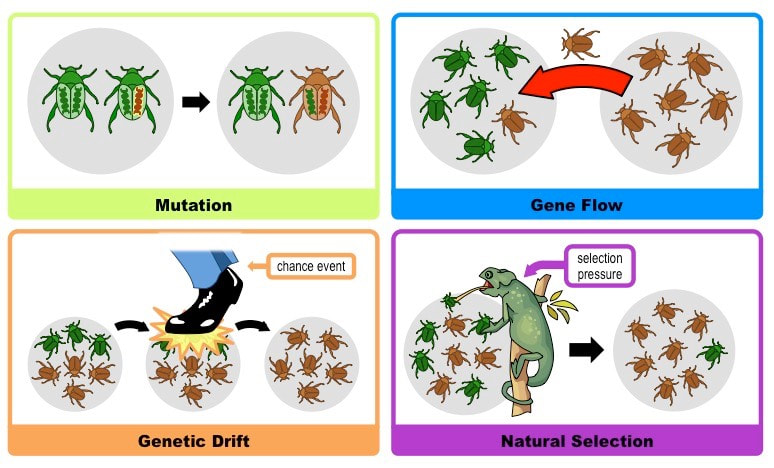
Source Image: mysciencesquad.weebly.com
Download Image
Change in allele frequencies due to natural selection – YouTube Natural selection only acts on the population’s heritable traits: selecting for beneficial alleles and thus increasing their frequency in the population, while selecting against deleterious alleles and thereby decreasing their frequency. Scientists call this process adaptive evolution. Natural selection does not act on individual alleles, but

Source Image: m.youtube.com
Download Image
Evolution of Populations Evolution by natural selection occurs when certain genotypes produce more offspring than other genotypes in response to the environment. It is a non-random change in allele frequencies from one generation to the next.

Source Image: zo.utexas.edu
Download Image
Are humans still evolving? – BBC Science Focus Magazine The change in frequency of the dominant allele ( Δp Δ p) after one generation is expressed by the equation. Δp = sp0q20 1 − sq20 (20.2.5) (20.2.5) Δ p = s p 0 q 0 2 1 − s q 0 2. where p0 p 0 and q0 q 0 are the initial frequencies of the dominant and recessive alleles respectively. Substituting, we get.

Source Image: sciencefocus.com
Download Image
Unraveling the Mystery of Evolution: Natural Selection and Life’s Diversity – English Plus Podcast Oct 31, 2023If we also know that the frequency of the I B allele in this population is 0.14, then the frequency of the i allele is 0.6, which we obtain by subtracting all the known allele frequencies from 1 (thus: 1 – 0.26 – 0.14 = 0.6). A change in any of these allele frequencies over time would constitute evolution in the population.

Source Image: englishpluspodcast.com
Download Image
Impact of selection on allele frequency spectrum and gene genealogy in… | Download Scientific Diagram Figure 1. Different types of natural selection can impact the distribution of phenotypes within a population. In (a) stabilizing selection, an average phenotype is favored. In (b) directional selection, a change in the environment shifts the spectrum of phenotypes observed. In (c) diversifying selection, two or more extreme phenotypes are

Source Image: researchgate.net
Download Image
IB HL 10.3.U1 & 10.3.U2
Impact of selection on allele frequency spectrum and gene genealogy in… | Download Scientific Diagram 5.0 (5 reviews) Natural selection changes allele frequencies because some _______ survive and reproduce more successfully than others. Click the card to flip 👆 individuals Click the card to flip 👆 1 / 32 Flashcards Learn Test Match Q-Chat Created by shanksnicky Students also viewed Ch. 23 AP Bio Quiz 5 terms mattchuritch Preview
Evolution of Populations Unraveling the Mystery of Evolution: Natural Selection and Life’s Diversity – English Plus Podcast The change in frequency of the dominant allele ( Δp Δ p) after one generation is expressed by the equation. Δp = sp0q20 1 − sq20 (20.2.5) (20.2.5) Δ p = s p 0 q 0 2 1 − s q 0 2. where p0 p 0 and q0 q 0 are the initial frequencies of the dominant and recessive alleles respectively. Substituting, we get.